Female Internal Genital Organ
These are situated in the lesser pelvis and include the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus and vagina.
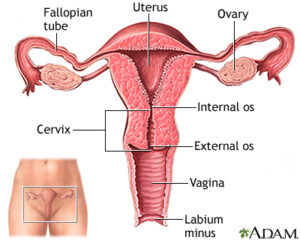
The Ovaries:
These are paired female sex glands situated one on each side of the uterus. Each ovary is almond shaped, greyish pink in color. It is 3cms long 1.5cms broad and 1cms thick. The Ovaries are variable mobile and may change their position according to the state of surrounding organs for example intestines.
https://shahsana.com/female-reproductive-system/
Structure:
Surface of the ovary is covered with a layer of cubical cells in young female which become flattened later in life.
Ovarian Follicles:
At birth cortex of the ovary consists of primary ovarian follicles which are premature germ cells at puberty some of these follicles mature into graafian follicles one of which ruptures every month (Ovulation).
Functions Of Ovaries:
The ovary is the organ in which the female gametes are stored and developed prior to ovulation.
Fallopian Tubes:
These are two tubes attached one on each side of the uterus in the upper margins of broad ligaments of uterus. Each tube is 10cms long, medial end opens into the superior angle of the cavity of uterus and lateral end opens into the peritoneal cavity. Each tube has four parts.
1.Infundibulum.
2.Ampulla.
3.Isthmus.
4.Intramural Part.
Uterus:
It is a hallow muscular organ which lies in the pelvis between Rectum and urinary bladder. It is 7.5cms in length, 5cms in breadth and 2.5cms in thickness. It is 30-40 gms in wright. It is shaped like an inverted pear. It is divided into three parts.
- Body
- Isthmus
- Cervix
Body:
If forms 2/3 rd of the whole length of the uterus. Its walls are 1-2 cms thick. At its upper end on each side fallopian tubes enter its walls to open into the uterine cavity. The part of the body above these opening is known as FUNDUS.
Isthmus:
It is a small area (6-7 mm) of uterus which lies at the junction of body and Cervix. In the pregnant uterus it forms the lower segment. The constriction between body and Cervix is the “Internal Os”. The isthmus lies below the internal Os.
Cervix:
It is the Apex of the pear shaped uterus. It is 2.5cms in length and projects (hangs) into the Vault of Vagina. The tip of the uterus is known as cervix.
Structure of Uterine Walls:
The walls of uterus consist of three layers. These are:
(1) Endometrium
(2) Myometrium
(3) Perimetrium
Function Of Uterus:
after puberty, the endometrium goes through a regular monthly cycle . the menstrual cycle prepares the uterus to receive, nourish and protect fertilized ovum.
Cervix:
It is the Apex of the pear shaped uterus. It is 2.5cms in length and projects (hangs) into the Vault of Vagina. The part which lies above the vagina is known as Supramarginal part and the part which lies inside the vagina is known as vaginal” part. Upper and lower ends of cervix are constricted and are known as Internal and External Os Respectively. The cervix has a narrow canal between Internal and external Os which connects the uterine cavity with the vaginal canal.
Ligaments Of Uterus:
Certain ligaments give support to the uterus. These are:
(1) Round ligament
(2) Broad ligament
(3) Ovarian ligament
(4) Uterosacral ligament
(5) Cardinal ligament
(6) Pubocervical fascia
Blood Supply
Arteries:
Internal Iliac Arteries.
Veins:
Uterine veins.
Vagina:
It is an elastic, fibromuscular tubular structure which lies between urinary bladder and Rectum. The cervix projects through its blind end (vault. Through the anterior end or Introitus its communicates with vulva. In virgins introitus is closed by a membrane known as HYMEN. At the vault four deep pouches are formed by the projection of cervix. These are anterior, posterior and two lateral pouches or fornixes according to their relation with the vaginal part of cervix
Structure
It consists of three layers.
(1) Stratified squamous Epithelium thrown into folds.
(2) Fibro muscular
(3) Fibrofatty layer.
Function Of Vagina:
The vagina acts as the receptacle for the penis during sexual intercourse and provides an elastic passageway through which the baby passes during childbirth.
ARTERIES:
Internal Iliac Arteries.
VEINS:
Internal Iliac Veins.