CELL
DEFINITION:-
Cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life. Size of an individual depends upon the number of cells and not on the size of the cell. Average size of a tissue cell is 10 – 20 um on the other hand small lymphocytes of blood are 6.5 um in diameter and ovum may have a diameter of 250 um.
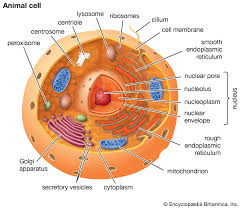
Components Of A Cell:
1. Cell Membrane.
2. Protoplasm -cytoplasm and Nucleus.
Protoplasm is bounded by cell membrane. Main mass of protoplasm is formed by cytoplasm in which on or occasionally more than one nucleus is found.
Cell Membrane:
It is a very thin and elastic membrane and has the property of self repair after damage Itis made up of lipids and proteins.
Content Of Cytoplasm
Cytoplasm consist of a water solution of salts ,proteins ,carbohydrates, lipid and Ribonucleic Acid . cytoplasm is in solution or Jelly from content of cytoplasm can be divided into two groups.
1.Organelles.
2.Incusions.
Organelles:
These are specialized parts of living substance which are permanent.
These include:
- Mitochondria.
- Golgi bodies.
- Centrosphere.
- Lysosomes.
- Membranes.
- Microtubules.
Inclusion:
These are products of cellular activity and are of temporary nature
This includes:
- Fat droplets.
- Pigment.
- Granules.
- Secretion granules.
- Glycogen particles.
- Crystals
Organelles
1.Mitochondria:
Thay are in the from of granules (0.5-2 um)or rods (5 um in length). They are responsible for release of energy to regulate cell metabolism. They are capable of transverse division.
2. Golgi Apparatus:
It consist of network of threads of Variable thickness located either close to the nucleus or on the sides. Golgi apparatus is concerned with secretions of the cell.
3. Centrosphere:
It is a small area of condensed Cytoplasm close to the nucleus and consist of two small dot like bodies known as centrioles. It is concerned with cell division. It is absent in highly specialized cell, that have lost the power of division for e.g. nerve cells.
4. Lysosomes:
These are small member bound structure of the size of mitochondria. They contain enzymes and are concerned with intercellular digestive processes.
5. Microtubules:
These are long tube – like structures several um in length. They are 2030 nm in diameter. They converge onto the centrosomes and are seen in increased numbers during cell division. They also act as cyto skeleoton and are found where cellular stiffening is required.
6. Endoplasmic Reticulum:
It is a system of interconnecting membrane lined channels. These channels are either flattened sacs or tubules . This channel system is of two types:-
1. Rough endoplasmic Reticulum:
2. Smooth endoplasmic Reticulum:
INCLUSIONS
1.Fat Droplets:
Small fat droplets may be seen scattered throughout the cell. Their number is increased in certain diseases.
2.Pigment Granules:
Different cells contain pigment granules of different kinds. There are three types of pigments formed by the cells. These are melanin, lutein and lipochromes.
3.Secretory Granules:
These are protein in nature and are in close contact with endoplasmic reticulum.
4.Glycogen Particles:
Glycogen particles are present in finely divided form. They are commonly found in liver cells, cartilage cells, muscle cells, white blood cells etc.
5.Crystals:
They are protein in nature and are present in very few cells for example liver cells, cells of testis etc.
THE NUCLEUS
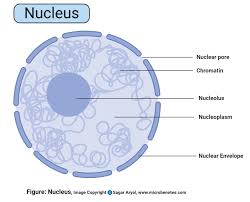
Nucleus of each cell is a spherical or ellipsoidal body 4-10 um is diameter separated from the surrounding cytoplasm by nuclear membrane. It is of vital importance to the cell and if it is lost the cell cannot live long and cannot divide.
It is commonly found in the center of the cells but in some cells adipose cells or secretory cells it is pushed to one side.
Nucleus contain one or more nucleoli which are spherical bodies containing RNA. These are concerned with protein pynthesis.
1.Nuclear Membrane:
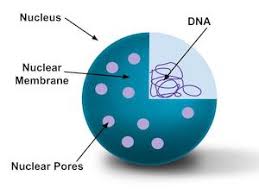
It consist of two layers separated by space and posses pores. Through these pores nuclear RNA can enter the cytoplasm.
Inside the nucleus there are thread like structures made up of DNA and protein. These are known as chromosomes. They form a network known as chromatin network. Number of chromosomes remains constant for that species of organism.
Material inside the nuclear membrane in which chromosome and nucleoli are dispersed is known as “Nuclear Sap” or “NUCLEAR MATRIX”